Intelligent Bypass switch
A Bypass Switch works in tandem with inline security and performance tools—including IPS, WAF, DDoS protection, DPI, and PCEF systems—to ensure continuous network connectivity and eliminate downtime caused by tool failures or power loss. Unlike traditional passive bypass switches, which require control software to be installed on the inline security tool and depend on external signal cables (typically USB or RJ11) to manage switching states, this approach may fail if the inline device crashes and is unable to trigger the bypass mechanism.
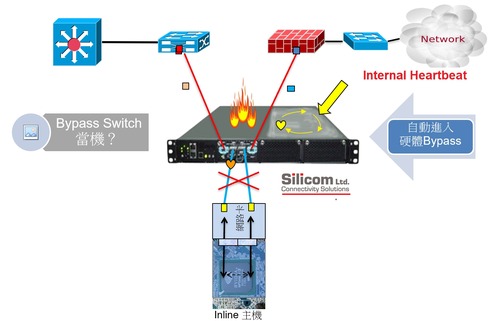
The new generation of intelligent bypass switches overcomes this limitation by generating its own heartbeat packets, which pass through the inline device and return to the switch. If the heartbeat response time exceeds a predefined threshold, the system automatically switches to Bypass, Tap and Linkdrop mode—ensuring continuous network connectivity and preventing downtime even when inline tools become unresponsive. Thanks to the high reliability and security of its inline connectivity, many users also deploy the Bypass Switch as a TAP Switch to replicate live network traffic to passive monitoring tools such as Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), Data Loss Prevention (DLP), or Database Activity Monitoring (DAM) solutions.
These tools help inspect traffic for potential intrusions or malicious activity hidden within the network. In addition, before switching to a full inline architecture, users can operate the device in TAP mode to validate and test inline tools. Once verified, the setup can be seamlessly converted to inline mode through simple configuration—eliminating the need for any physical recabling and ensuring smooth deployment.
◆An Active Bypass Switch achieves bypass functionality by dynamically changing routing paths to maintain network continuity. Before entering bypass mode, the system performs a health check on the connected inline device to ensure its operational integrity. The Bypass Switch conducts this health monitoring using self-generated heartbeat packets, which pass through the inline tool as part of the normal traffic flow. If the inline tool experiences a failure—such as a system crash, software malfunction, disconnection, or power loss—causing the heartbeat packets to fail to return within the predefined interval, the Bypass Switch automatically alters the routing path and switches into Bypass, TAP, or Linkdrop mode to preserve network stability and minimize disruption.
◆A Passive Bypass Switch achieves bypass functionality through changes in the hardware circuit loop, typically triggered by alterations in the hardware’s physical state. The switch itself is designed to automatically switch into Bypass or Link-Down mode in the event of a power failure, preventing network disruption and ensuring continuous data transmission even when the bypass switch loses power. In certain high-end models, such as those from Silicom, the device is equipped with a Watchdog Timer (WDT) that monitors its own operational status and can proactively initiate a passive bypass state when necessary to protect network continuity.
Dual Heartbeat Mechanism — Double Protection Against Network Downtime
Most organizations deploying Bypass Switches share a common concern — that the switch itself could become a single point of failure. A design that activates bypass mode only during a power loss is not enough for a device running on an internal operating system. Yet, many products on the market today overlook the risk of software-level instability within the switch itself. With more than 30 years of innovation in bypass technology, Silicom — an industry pioneer from Israel — identified this challenge early on and built a smarter solution. Silicom’s Intelligent Bypass Switches integrate not only the standard external heartbeat monitoring, but also an internal heartbeat that delivers redundant protection against both hardware and software failures. This dual-layer design ensures the switch automatically enters bypass mode in the event of a power failure or software crash, providing unmatched reliability and true fail-safe resilience across mission-critical networks.

